Agent SNMP Online UPS
The reliable solution to control, manage and monitor your computer or Power Conditioner!
The SNMP concepts
The SNMP model defines two entities, which works in a client-server mode.
The SNMP server is called a SNMP agent and is located on the device to monitor. The client part is the SNMP manager in charge of the data collection and display. The SNMP version 3 names it the client entity instead of SNMP agent. The SNMP agent listens to requests coming from the SNMP manager on the UDP port 161, while the SNMP manager listens to alarms “TRAP” coming from the agent on port UDP 162.
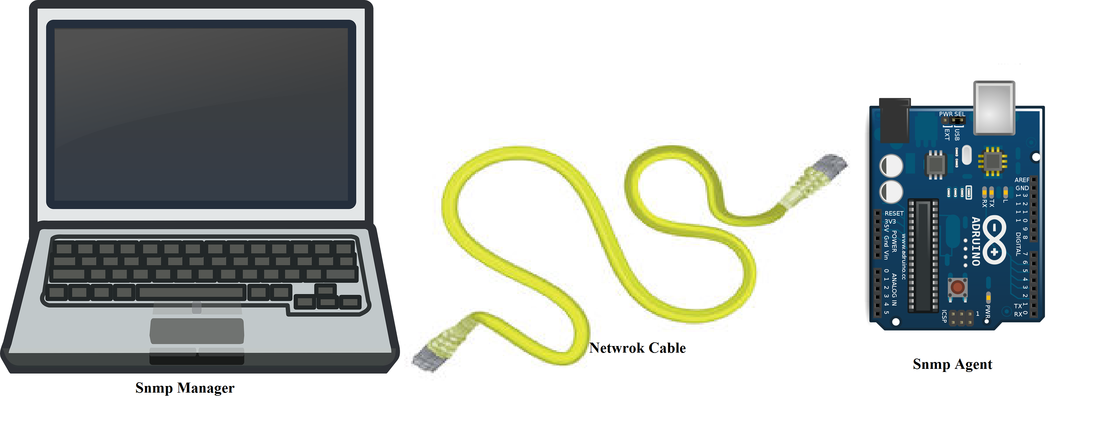

The SNMP manager
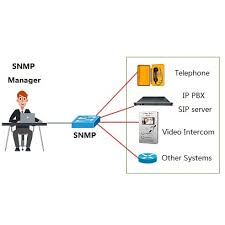
The SNMP manager should be installed on a powerful system connected to the enterprise network. Another common name for it, is management station.
The SNMP manager job is to acquire with SNMP requests, information about devices connected to the network. Gathered information are then processed and displayed in tables, graphs, gauges, histograms, for an easier interpretation by human being.
The management station includes the following components:
The graphical user interface
Use to display in a friendly manner collected data.
The database
The database is used by the manager to store collected data.
The transport protocol
Protocol is used to communicate between manager and agent.
Le SNMP engine
This is the kernel of the application. It manages all the tasks like an orchestral chief.
Agent management profiles
This is a set of rules that defines how to access to the agents. All this profiles help to build the topology map.
The SNMP agent
The agent is a mix of software and hardware or only software and is located in the device. Most of network devices are equipped by default, other systems having a standard operating system are able to behave like an agent by running a simple process. Most of them, Windows platform, Novell Server, Unix and Linux systems own their agents. Hubs and MAU, for most of them are also manageable.
Agents are composed of:
| A transport protocol stack | Responsible for sending and receiving SNMP packet |
| An SNMP engine | Process requests and formats data. |
| A management profiles | These are the rules that control access to MIB variables and manage which requests are authorized. |